notes for chapter 7, 6-29
journal entry - a patient comes to the dr complaining that his body doesnt move like it used to. the joints have been ground down so bones are rubbing together and wearing away - he doesnt have a physically intense job - - the dr figures it out as soon as she sticks patient w/ needle - what sense is this patient missing
he can't feel pain
nociceptive - can't feel pain from outside
interoceptive - can't feel pain from inside.
sensory areas of the cortex
- primary sensory cortext - direct input mainly from thalamix relaty nuclei
- ie striate cortex recives input from LGN
- secondary sensory contex - inpyt from pri and sex cortex w/in sensory system
- association cortex - input from more than one sensory system - usually from 2nd sens system
principles guiding sensory cortex interactions
- heirarchal org.
- specificity and complexity increases w/ each level.
- sensation - detect a stimluus
- perception - understanding stimulus
- functional segregation
- color/movement have own modules
- parallel processing - like computers - do it faster
Sensory system organization
picture - in book figure 7.2
- multiple specialized areas @ multiple levels, interconnected by many parallel pathways
- the binding problem - how does brain finally integrate info- but there are corticofugal pathways that allow higher areas to influence lower areas - higher being cortex, lower being subcortical
- Visual cortex
- Primary (v1) - posterior occiptal lobe
- secondary
- prestriate cortex - band of tissue around v1
- inferotemporal cortex
- Association - various areas, largest single areas is in posterior parietal cortex
- bc we have parallel network - if one thing breaks, it will still work around it.
- study of Scotomas - area of blindness resulting from V1 damage
- hemianopsic - last perception in half of visual field
- blind in corresponding contralateral visual field of both eyes
- deficit may or may not be readily detected bc of completion (like blond sport)
- seeing stars is a temporary scotomas
- Blindsight
- ability to respond to visual stimulus even w no conscious awareness of the stimulus
- putting coins in slot - they can do it even if they cant see it
- may still be connections in v1 allowing for reactions w/p awareness
- may be that message gets to brain by connections that dont pass thru scotoma.
- -video about blindsight patient who cant see - but can process stuff - cool. - kirsten - ask me and i'll explain it better - about movement
- "vision is not entirely seeing there can be a something to respond to visual info and being able to see"- messed up quote :)
notes continued
- without this zombie in our brain helping us have autopilot - like driving
- grahm's blindness - cant see, but can sense- perception w/o sensation/conciousness- like video
- like subjective contours - white triangle, cube, pyramid - figure 7.6
dorsal and ventral streams
- dorsal stream - where - /control of behavior
- v1 to dorsal prestriate to posterior parietal
- ventral stream - what - /conscious perception
- v1 to ventral prestriate to inferotemporal
- both where and what ///behavior/percetion distinctions are supported by effects of damage
- not so much kinds of info - but the use to which that info is put - do we use it to interact w/ objects or see them or what
photo - figure 7.9
theres lots of types of chairs - so object recog just tells us - yes this is a chair
Aperceptive agnosia - difficulty in perceiving basic elements that make up an object - dependent on amount and location of damage- cant percieve X to cant perceive complex
cant copy pictures - like stick drawings
Associative Agnosia
- difficulty in assigning meaning to an object it cant be recognized
can copy pictures
cant build whole representation for object
cant get generalize categories sometimes
the man who mistook his wife for a hat
Prosopagnosia - cant recog faces agnosia for faces
can say this is a face - but not bc
damage to hippocampal formation
also have trouble saying which cow or which chair
can be damage to ventral/what stream
thus unconscious recog can be hypothesized
has been supported - altered auto responses.
fusiform face area- activity increased during face recog but not recog for other objects
areas in ventral stream may be specific to humans, cats , houses, other broad categories
each area responds to each class but there is a great overlap in areas.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Audition
- actual sound waves
- figure 7.10
- higher the amplitude - louder the sound
- timbre- how deep the tone is
- pure - only in lab
- sound waves>auditory canal>tympanic membrane>ossicles(3 bones register vibration)>[thru the]oval window>cochlea fluid[snail thing]>organ of corti[trasmits to neural signal]
- semicircular canals - help us w/ vestibular/balance system - filled w/ fluid, like a level
- when you drink too much, alcohol is a toxin in the semicircular canals (in the ears), stops them from working as well - also why you throw up.
- basically your semicircular canals get drunk
- figure 7.12
- Organ of Corti
- the cohleas internal mebrane, it is the auditory receptor organ
- composed of 2 membranes
- basilar membrane - aud recept, hair cells, mounted here
- tectorial membrane - rests on hair cells
- charlotte - missing some part that helps to hear deep sounds
- cant hear as well
- stimulation of hair cells triggers AP in auditory nervels
- Cochlear coding
- diff frequencies produce maximal stimulation of hair cells @ diff points along basilar membrane
- tonotopic org. - organized by tone
- a network of auditory pathways
- auditory nerve axons>ipsalateral[on same side, doesnt cross over] cochlear nucleus >superior olives>inferior colliculi>medial geniculate nucleus(thalymus)>primary auditory cortex
- figure 7.13 kinda
- process on both hemispheres, helps w/ location
Auditory Cortex
- 2-3 areas of primary auditory cortex
- about 7 areas of secondary
- functional columns - cells of a column respond to same frequencies
- tonotopic organization
- secondary areas dont respond well to pure tones and have not been well researched
- Sound localization
- mediated by lateral and medial superior olives
- both structures react to differences in what is heard by two ears
- medial - arrival time differences- which ear gives half
- lateral - amplitude differences
- both project to superior and inferior colliculi
- Auditory Agnosia
- hear, not recog what hear.
- can be hard to recog temporal (timing) parts of sounds (gaps or durations of sounds)
- makes understanding speech difficult
- verbal 0 cant detect pattern or meaning
- non-verbal - trouble distinguishing non words - doorbell/phone/barking
- mixed
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Somatosensation
- exteroreceptive- touch(mech stimuli), temperature (thermal), pain (nociceptive)
- Cutaneous receptors
- free nerve endings , temp and pain
- Pacinian copuscles (shapes like onions)
- adapt rapidly, large and deep
- sudden displacements of skin
- Merkel's disks - gradual skin indentation
- photo : ruffini ending merkels disks etc
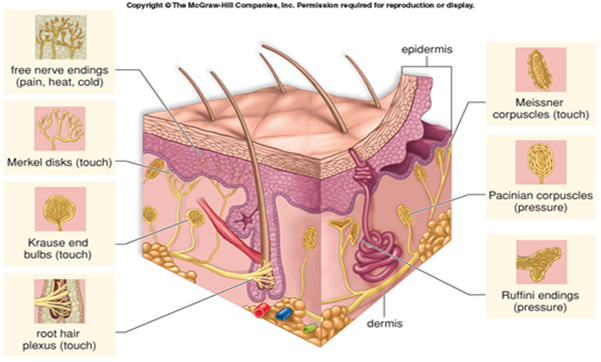
- respond to ∆
- stereognosis - identify objects by touch
- dermatome - area of body innrvated by left and right dorsal roots of a given segment of a spinal cord -figure 7.16
- ascending somotosensory pathways
- dorsal columbn medial lemniscus system
- touch and prprioception
- 1st synapse in dorsal colum nuclei of the medula
- anterolateral system
- pain and temp
- synapse upon enter spinal cord
- Primary Somatosensory cortex (SI)
- postcentral gyrus
- somatotopic
- more sens = more cortex
- input mostly contralateral
- SII mainly imput from SI
- somatopic - imput from both sides of body
- somatosensory homonuculus
video person swap


